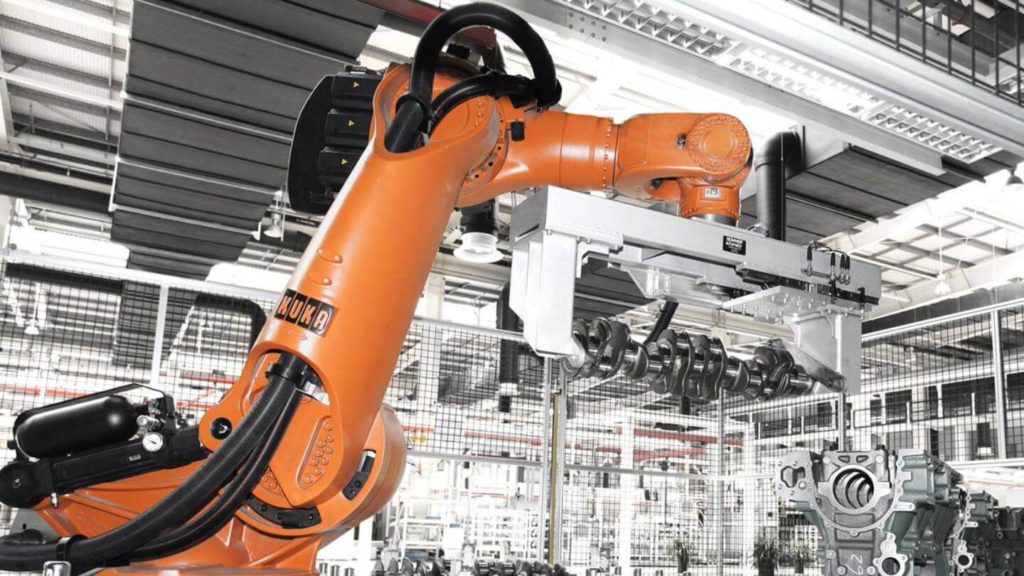

Professional 3D printers today use additional technologies - such as cloud connectivity, data analysis, automation and software integrations - to help manufacturers use each printer in new and innovative ways.
Adding these technologies to professional 3D printers is part of the digital transformation of manufacturing known as Industry 4.0 . Read this blog to learn what Industry 4.0 is in simple words, the role of today's professional 3D printers in Industry 4.0, and examples of how additive manufacturing platforms use Industry 4.0 technology to provide solutions to problems.
Defining Industry 4.0
McKinsey & Company defines Industry 4.0 as a name for a broader "digitalization of the manufacturing sector" - what this means in particular is the application of emerging technologies in production facilities to improve processes.
The main topics and features of Industry 4.0 include:
- The ability for different devices and machines within the factory - such as printers and sensors - to send and receive digital information from each other.
- Collection of data from sensors in machines and devices in the monitoring factory.
- The ability of technological systems 1.) to increase human decision-making and 2.) to facilitate the performance of dangerous physical tasks.
- Switch to intelligent, automated systems that require minimal human supervision.
Specific technologies that fuel Industry 4.0 include cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), industrial Internet of Things (IoT), data analysis, industrial robotic systems, professional 3D printers, and big data. Although these individual technologies were not specifically designed for use in smart factories, Industry 4.0 describes the growth and maturation of their application to factory settings.
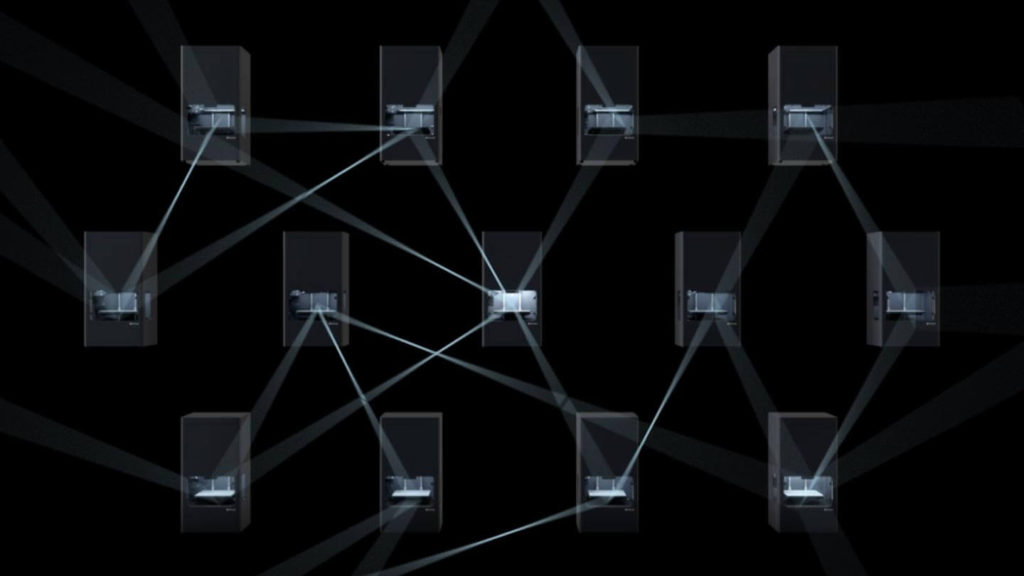
The link between Industry 4.0 and the add-on
Additive manufacturing is a technology typical of Industry 4.0. By converting digital inputs into physical outputs, digital inventory in the form of CAD files is uploaded to 3D printer software, resulting in conversion from a digital object to a physical equivalent.
In essence, it is a tool for the core set of Industry 4.0 technologies - such as cloud computing, intelligent automation, IoT devices, digital inventory and data analysis - to be directly applied to the manufacturing process itself. Whereas previously this was only applicable to selected, less demanding applications, the expansion of professional 3D printer technologies - such as expanding the supply of both composite and metal materials, as well as significant improvements in speed, reliability, accuracy and quality - allow convenient digitization of production processes for a much wider range of applications and on a larger scale than before. In a sense, 3D printing is the specific technology that is most iconic for Industry 4.0: among the list of individual technologies that shape it together,
While the capabilities of professional 3D printers have helped shape Industry 4.0, many Industry 4.0 technologies have also stimulated the growth of additive manufacturing. When first introduced, professional 3D printers were nothing more than separate hardware elements. Since then, additive manufacturing has grown with Industry 4.0, in today's full-featured 3D printing platforms with advanced 3D printing software capabilities, connectivity to devices in different geographic locations, a wide range of advanced analytics, and automated AI-driven features such as stand-alone AI verification. parts.
Examples of how 3D printers use Industry 4.0 technology
To allow manufacturers to get the most out of any professional 3D printer, additive manufacturing solution providers have integrated a core set of Industry 4.0 technologies into their 3D printer platforms.
Here are examples of technologies, how they complement professional 3D printers and how they solve manufacturers' problems:
Cloud computing provide connectivity between users and any professional 3D printer operated by an organization in different geographical locations. In fact, the user can jump on his laptop and start printing a repair part for a factory in another part of the world.
With digital inventory of parts like data elements, Stored in the cloud, this capability offers many advantages: manufacturers can avoid the need to stock up on large amounts of inventory and work effectively with a lean production model with just-in-time (JIT) production. In addition, the distributed production model allows consumers to avoid supply chain complications and simply receive parts faster by printing parts to the exact point of need when needed, instead of ordering a part in one place and sent to the place of need.
Software for today's professional 3D printers also provides a variety data analysis for its users. Organizations can track metrics such as material usage, quantities of user print jobs by time intervals, user printer frequency band, weekly uploads, and custom analysis fields. Printing times and the cost of a print job are calculated according to variables such as part size, material and fiber volume used to reinforce the plastic matrix. Using these analyzes can allow organizations to understand equipment use patterns and optimize resources accordingly.
Professional 3D printers are inherent automated - just pressing the "button"seal“It will take you from artificial intelligence to work in just hours or days without the need for practical intervention, management or human supervision. With in-house additive manufacturing, engineers don't have to worry about time-consuming procurement activities such as drawing, submitting purchase orders, and managing the multi-vendor bidding process.
More recently, the quality control of parts has been fully automated - during the production process, 3D printing software powered by artificial intelligence can check whether the printed part can be used immediately in the factory, automatically generating quality and traceability reports of the parts.
Professional 3D printers can also be used through 3D printing software APIs integrate with other major systems within an intelligent factory, such as through the Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) system. Print jobs can be initiated through any of these systems. If a user requests part of one of these systems, this system can trigger an automatic print job in each specific 3D printer.
What does this mean for manufacturers?
By integrating Technology 4.0, AM (Additive Manufacturing) technologies, it has allowed manufacturers to link their production to different geographical locations, enable a cost-effective production model with digital inventory availability, and automate many of the difficult tasks that come with manufacturing. parts.
As professional 3D printer technology continues to evolve, industry 4.0 digitization can be expected to reach an even wider range of digital applications.
The article is taken from Markforged. The original version can be found here: https://markforged.com/resources/blog/industry-4-0-and-professional-3d-printers?mkt_tok=ODcxLURJTS03MjMAAAGDnG5huuCTFcQEL_7d0bf3INyWrT90ja1lOof3a865Kk0hZFNNcucNKv_B-7zR4sEyiXaeimHLb5qt1HEEBKloLL1XzH–buJmXMIQ4y-4GGlM
0 Comments